What is Aromatherapy?
“The controlled use of essential oils to maintain and promote physical, psychological, and spiritual well being is called Aromatherapy.” ~ Gabriel Mojay
Aromatherapy is one of the oldest forms of treatments on earth which dates back to some 6000 years. Even older than our traditional Indian medicine called Ayurveda which is some 3000 years old. In this article I will be talking about how aromatherapy works in our body. In the subsequent blogs I will be writing about the healing powers of essential oils.
How Aromatherapy Works in our body?
Essential oils enter in our body by three main pathways:
- Nose by inhalation
- Skin by massage and
- Internal consumption (not recommended)
How aromatherapy works through our Nose?
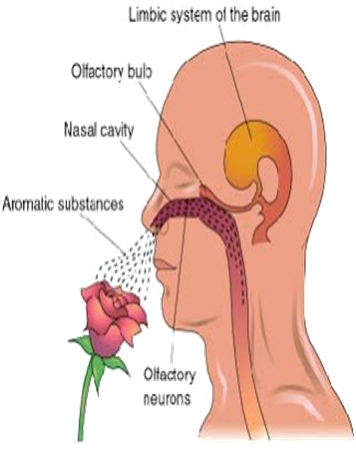
Have you ever noticed that when an essential oil is set in a diffuser, how fast its aroma spreads in the room? Why? Firstly, because molecules of Essential oils are very minute that helps them to spread very fast. Secondly, they are very volatile. Volatile means anything that turn from a liquid into a gas at room temperature or higher. This is the reason that all Essential oils universally have the ability to cross the blood brain barrier (BBB). What is blood brain barrier? Blood brain barrier is a protective mechanism of our body to allow only selective particles to enter the brain. Anatomically, Our brain’s capillaries are so closely wedged into one another that they form tight junctions. Due to this setup, there is selective permeability or it allows only those molecules to enter the brain that are smaller in size, are fat-soluble or are gases.
Now lets understand, what happens when we inhale the essential oils?When we inhale the aroma of essential oils, the molecules present in it, stimulate the olfactory bulb present in our nose which in turn sends a sensory stimulus through the olfactory nerve to the limbic system of our brain. What is Limbic system? Limbic system is that part of our brain where our moods, emotions & memories are functioned and controlled. Anatomically, This system is a complex set up which includes the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and several other nearby structures. Hypothalamus lies at the center of our limbic system and is responsible for regulation of blood pressure, heart rate, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal and the circadian rhythm sleep/wake cycle. Amygdala also called the emotional center of brain is responsible for emotions like anxiety, aggression, fear conditioning; emotional memory and social cognition. Hippocampus is responsible for our long term memory.
How aromatherapy affect the brain?
We just read in the section above how essential oils trigger the limbic system of our brain. Once the limbic system is triggered, our brain gets a signal to release certain neurotransmitters such as serotonin, endorphins, adrenaline etc. Serotonin is a brain calming neurotransmitter, endorphins are euphoric and non-adrenaline is brain stimulating hormone. This is how essential oils affect our mind and provide a feeling of relief.
For example, Aroma of Lavender Essential oil, Vetivar EO, Orange EO, Rose EO, sandalwood EO trigger the brain to release serotonin that has a calming effect on mind and promote sound sleep. They are useful in relieving stress, depression and anxiety. These are mind-calming Essential Oils (EO).
Similarly, Endorphins are said to be natural pain killers because when they are released there is an analgesic effect on the mind and body. Examples of Essential Oils that can trigger the release of endorphins are lavender oil and lemon oil. It is shown in research that when lemon essential oil was slowly diffused near a group of depressed patients over a period of 2 weeks, the patients were able to experience significant mood elevation. The results also indicated that the antidepressant dose necessary for the treatment of depression can be markedly reduced1. Lemon essential oil can be inhaled by putting 1-2 drops in your handkerchief. You will feel much energized. These are Euphoria producing Essential Oils (EO).
Another category includes Essential Oils that make you alert and wakeful.
These are mind stimulating essential oils. For example, Black pepper, lemon, jasmine & rosemary essential oils. Black pepper essential oil has been shown in research to appreciably increase epinephrine levels on inhalation (Haze et al 2002) and particularly where lethargy is a problem, not so if anxiety is high.
How aromatherapy works through the skin
The essential oils enter the skin pores owing to their small molecular size and reach the subcutaneous tissues. From there they reach the muscles & tissues; from muscle & tissues the active essential oil molecules go to the blood stream and to other body tissues & organs. Finally, they are excreted through the excretory organs.
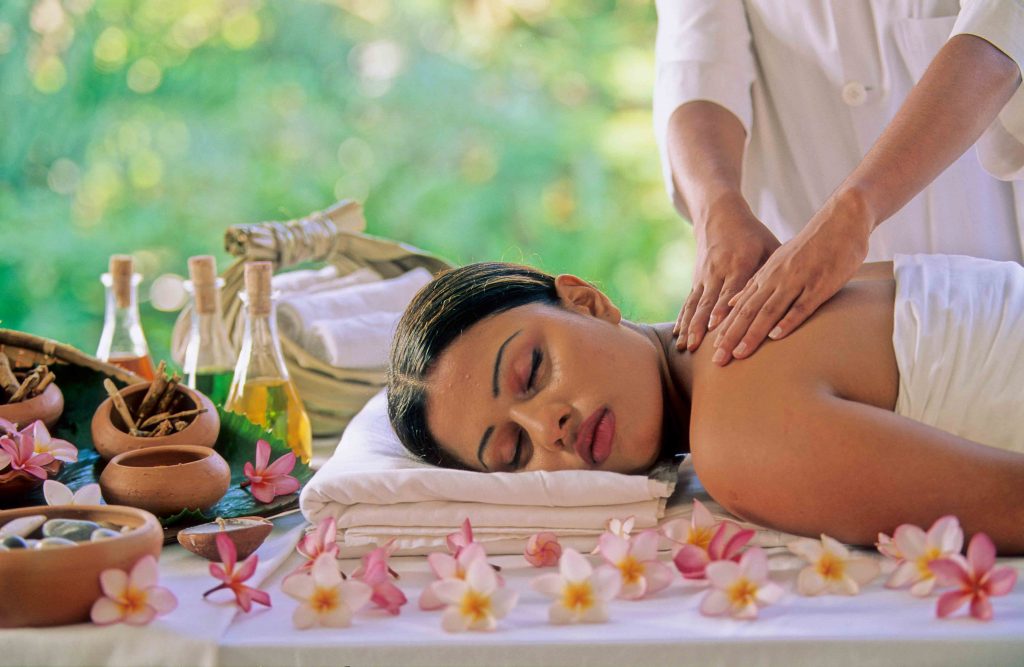

Essential oils enter and leave the body efficiently, leaving no toxins behind unlike any chemical or drug. Also there is no residual effect as they are eliminated very quickly through skin and other organs.
In various researches, the skin permeability effect of Essential oils have been discovered. As the oils absorb into the skin, the muscles relax and the therapeutic benefits manifest. They improve blood circulation, increase metabolism, speed up the healing process, boost the removal of toxins and increase muscle and joint mobility thereby reducing aches, pains, spasms and stiffness.

Whether inhaled or applied topically, essential oils calm, energize or stimulate our mind, body and soul. Always use pure organic unadulterated essential oils from a trusted supplier because only pure and therapeutic grade essential oils possess healing powers. Aromatherapy is safe, effective and a convenient complementary therapy. Unfortunately adequate research is lacking to support the claimed benefits of essential oils.
References:
1. De Souza D.P. et al. Essential Oils and Their Constituents: An Alternative Source for Novel Antidepressants. Molecules 2017, 22, 1290. To view online:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28771213
2. Haze et al. Effects of Fragrance Inhalation on Sympathetic Activity in Normal Adults. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 90, 247 – 253 (2002). To view online: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jjp/90/3/90_3_247/_pdf/-char/en






Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I in finding It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I’m hoping to present something back and help others like you helped me.